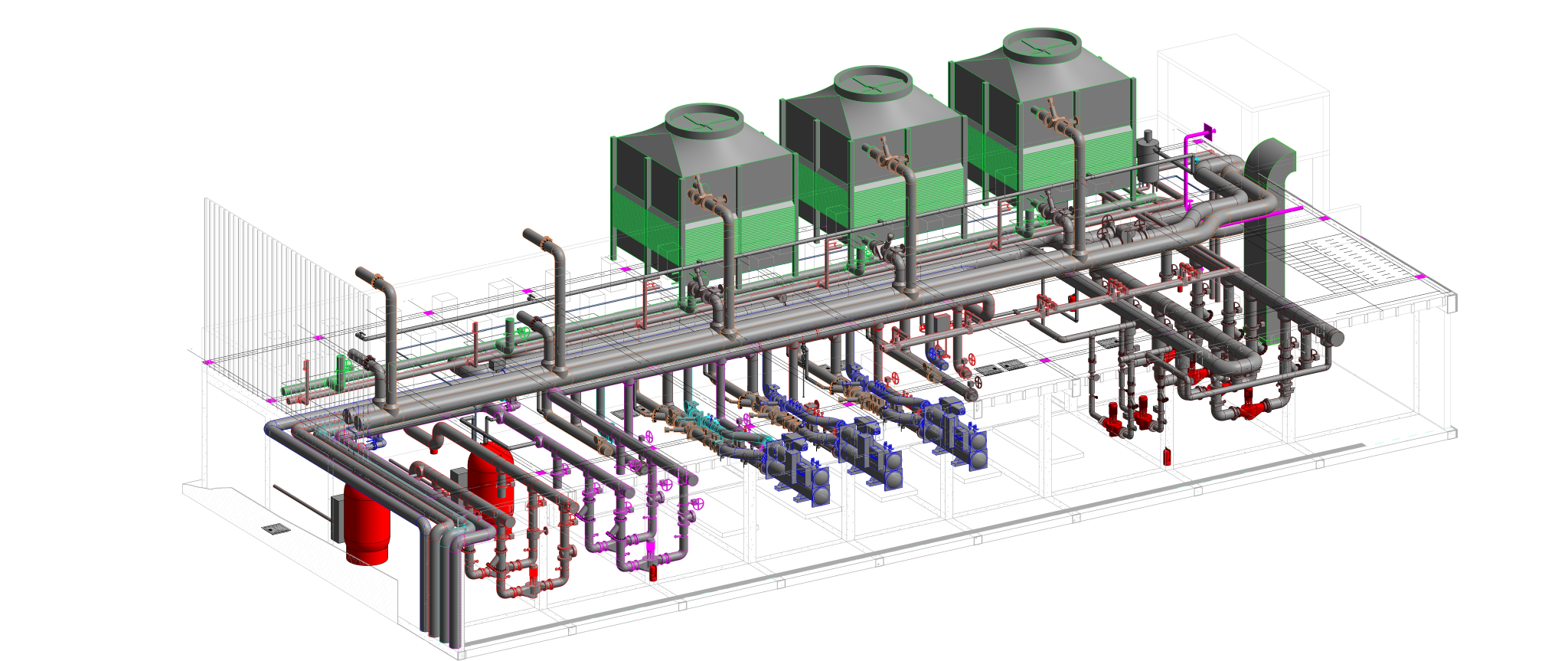
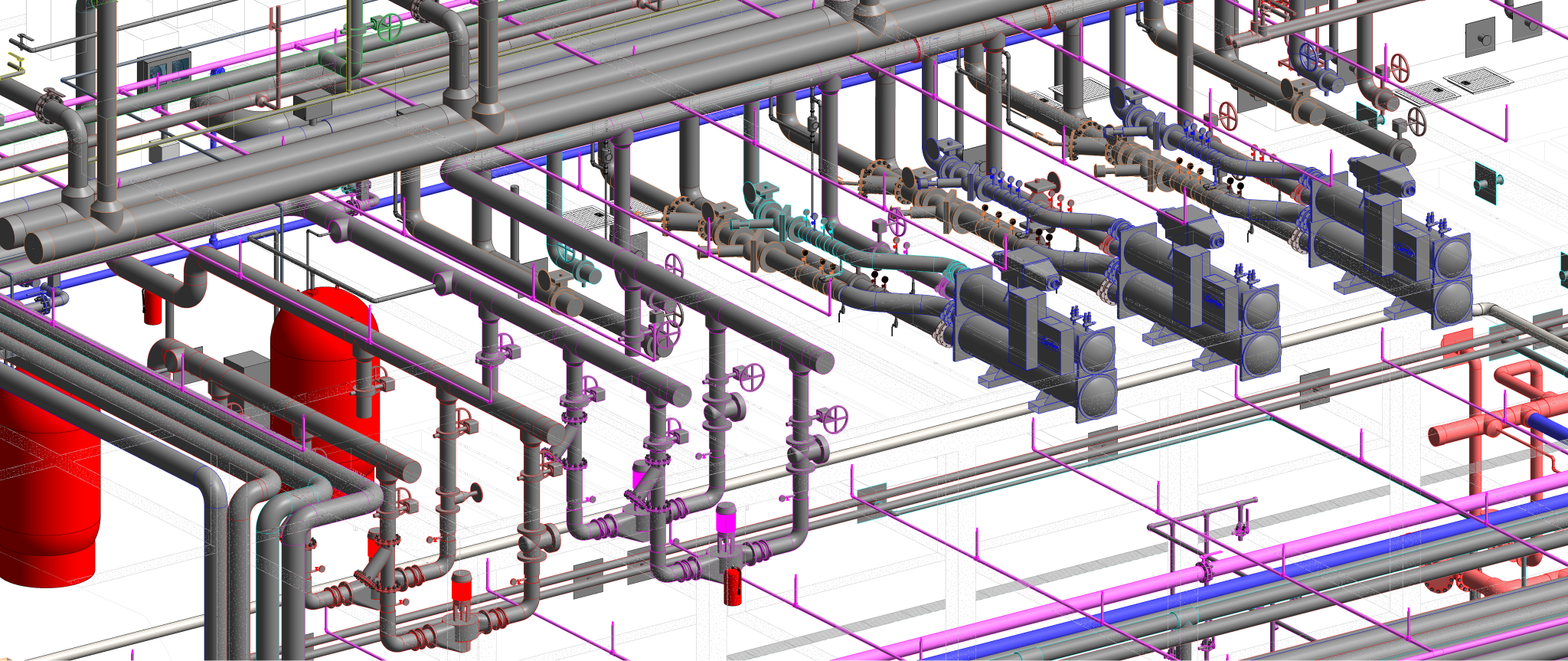
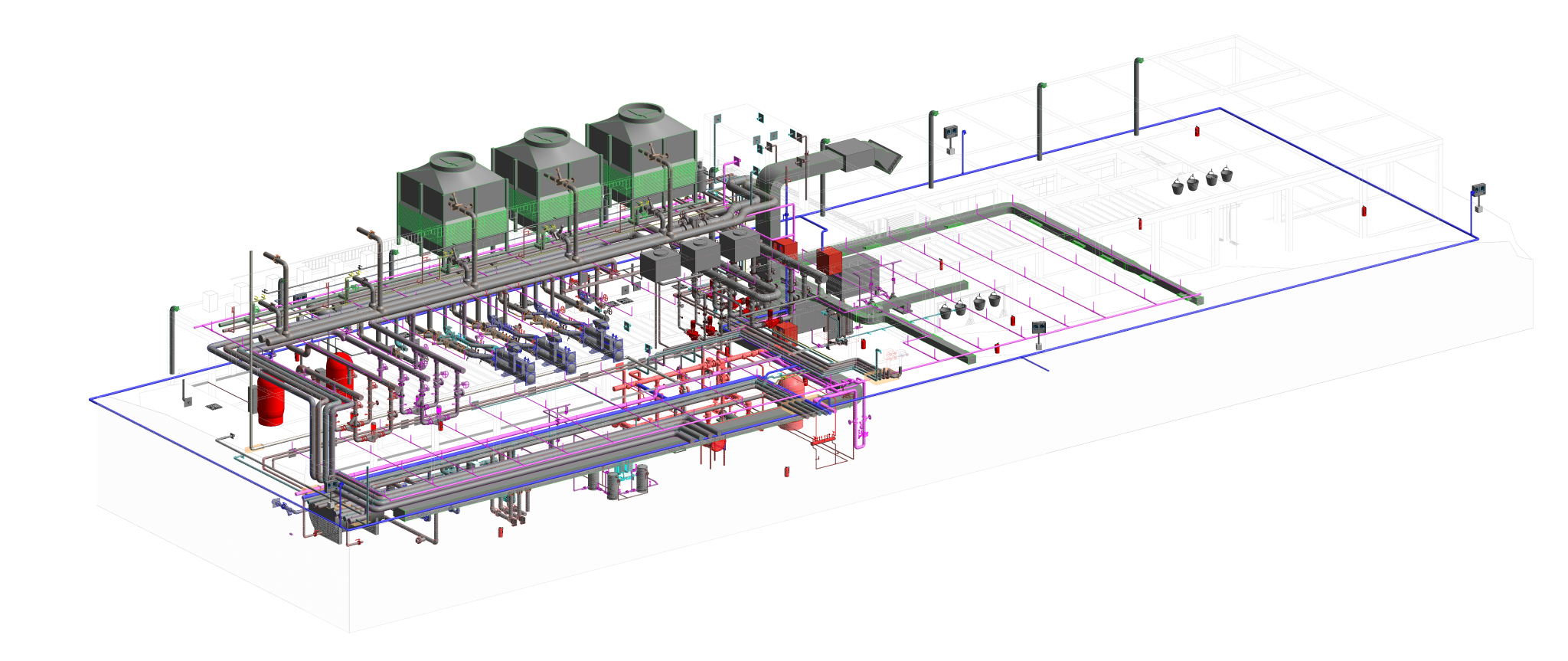
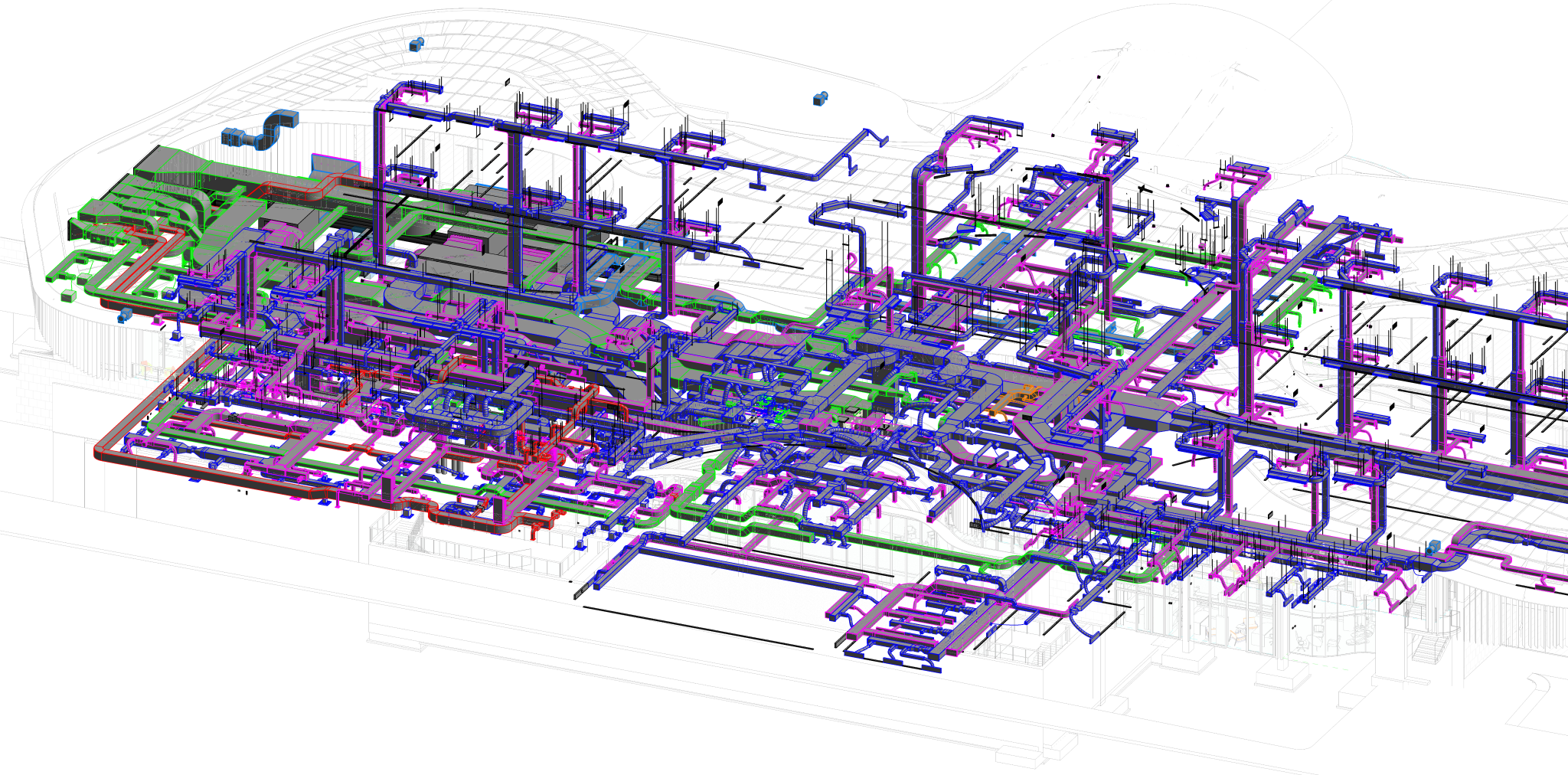
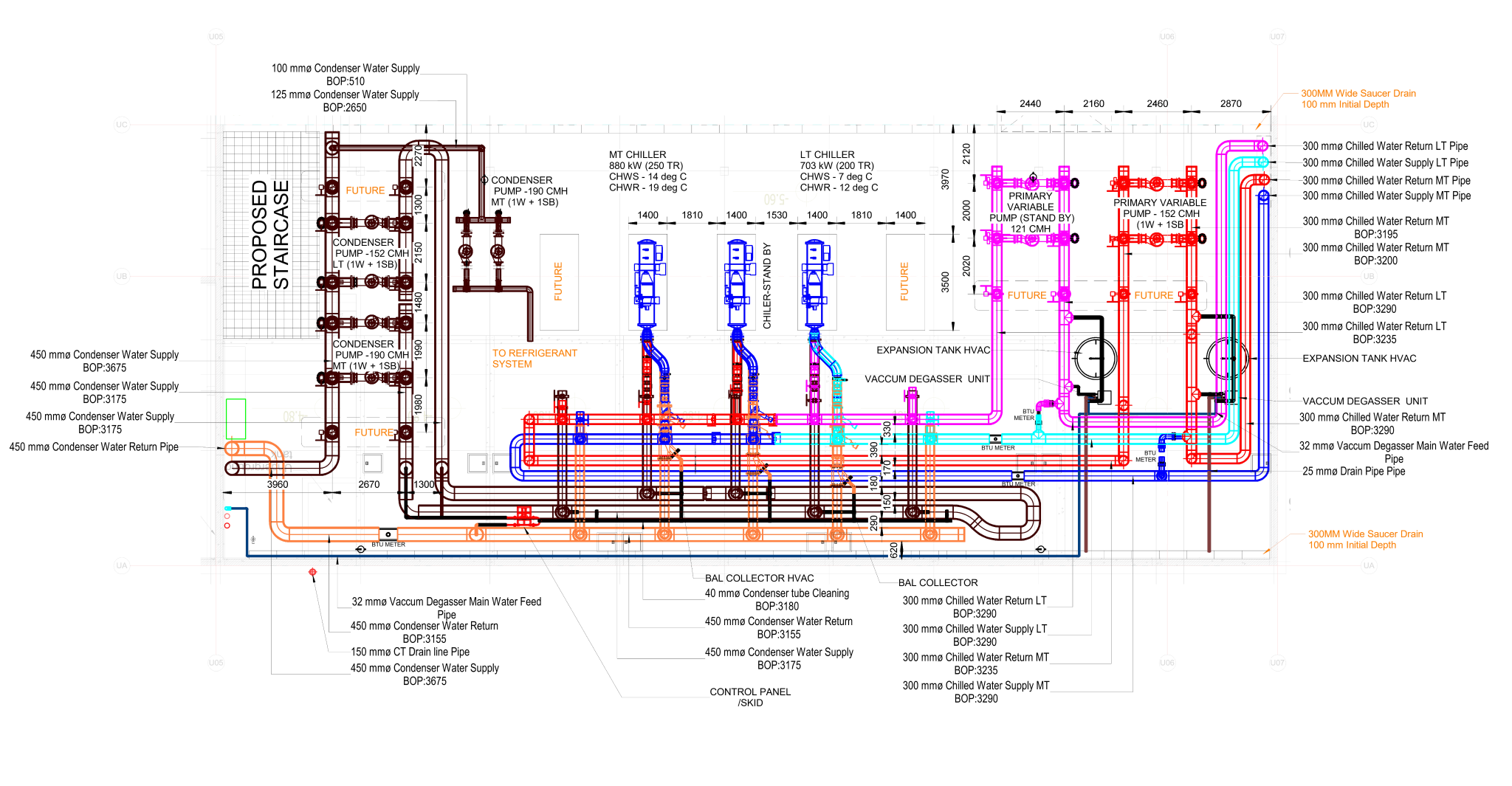
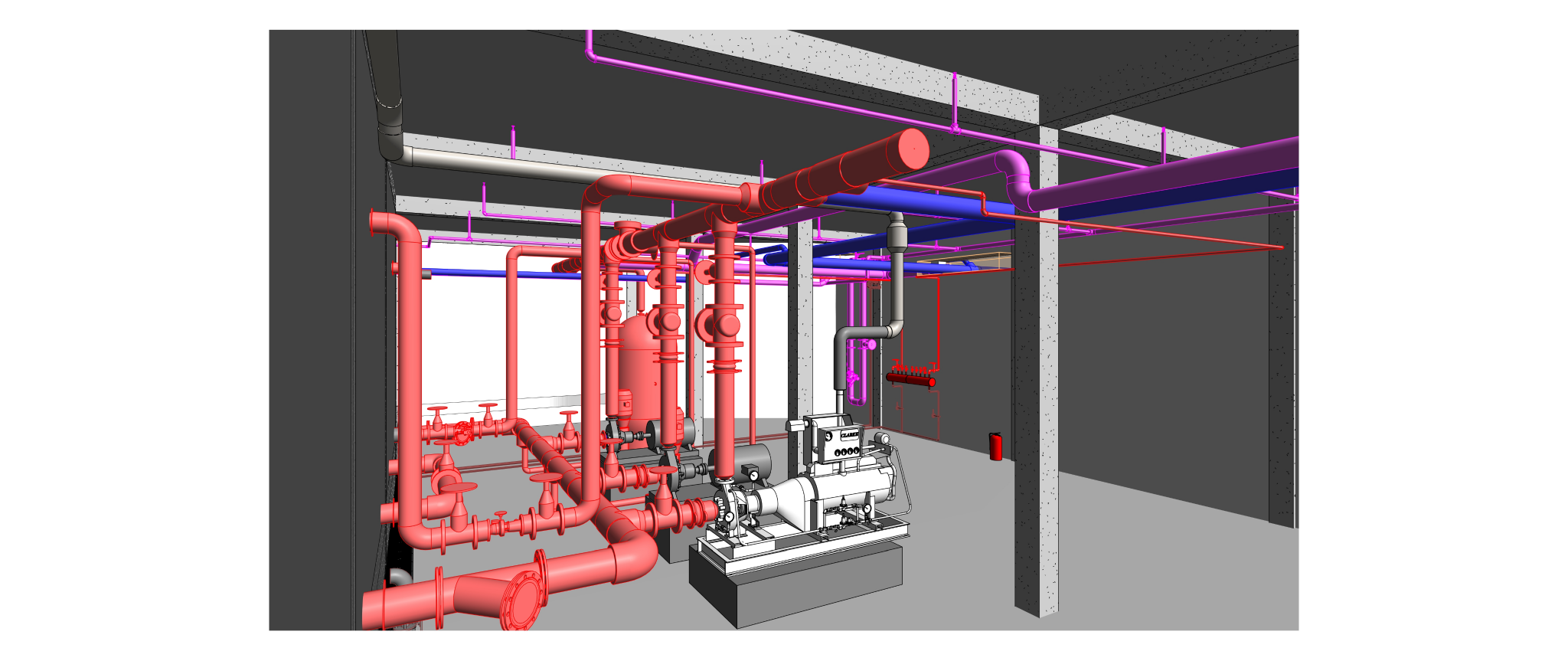
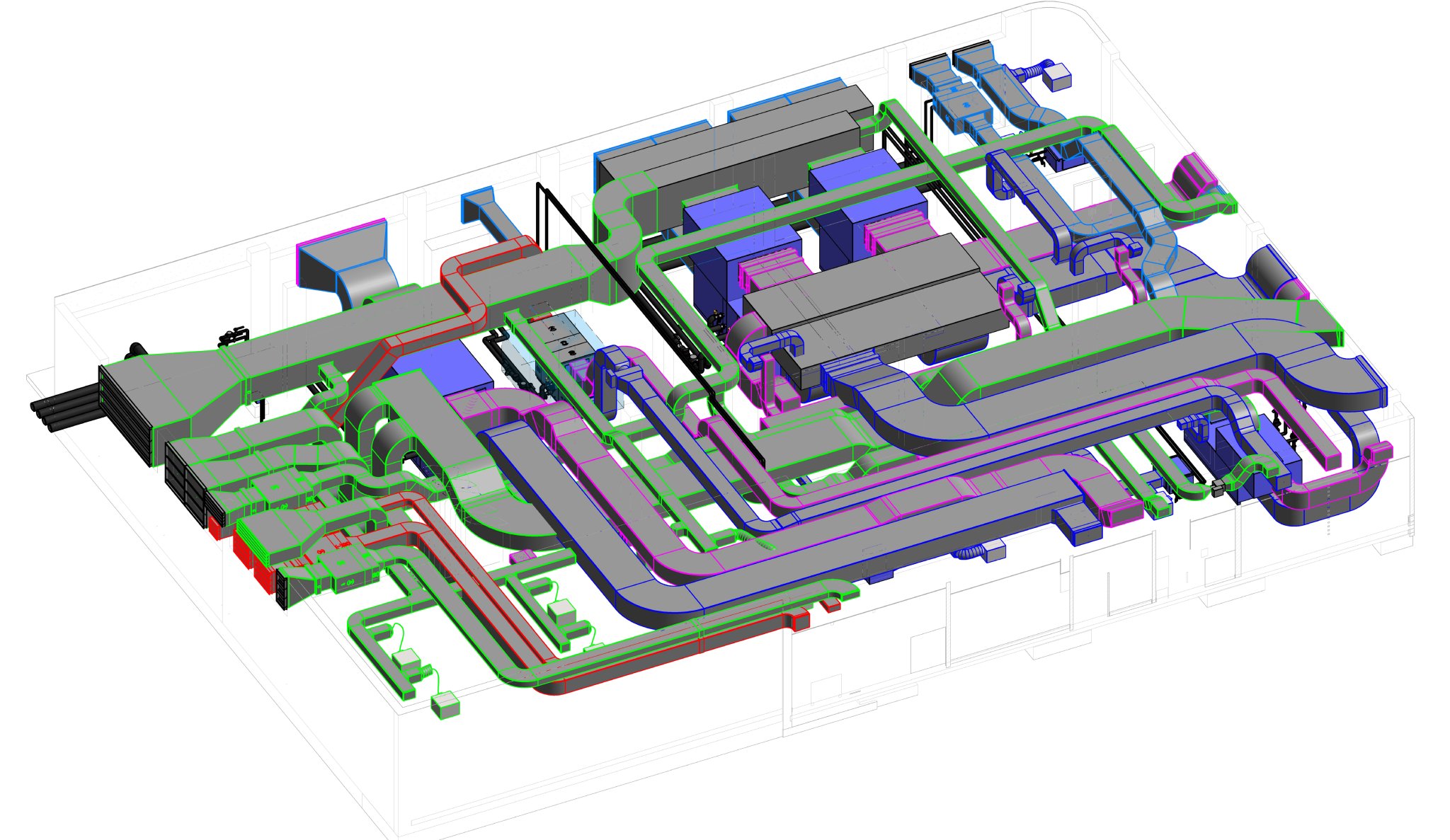
Building information modelling (BIM) is a transformative approach to the planning, design, construction, and management of buildings and infrastructure. Unlike traditional 2D drawings, BIM involves creating a digital model that encompasses not only the geometric representation of a structure but also a wealth of data related to its components, materials, systems, and performance attributes.
Some of the key components of BIM are:
- Geometry: BIM models include three-dimensional geometric representations of building elements, providing a visual understanding of the structure's form and layout.
- Data: BIM incorporates non-graphic information related to each building component. This can include material specifications, dimensions, cost data, performance characteristics, and maintenance requirements.
- Relationship: BIM enables the establishment of relationships and dependencies between different elements in the model. For example, connections between structural components or the impact of a change in one area on other aspects of the project.
- Collaboration: BIM facilitates collaboration among different stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers. This collaborative environment encourages real-time sharing of information and reduces the likelihood of errors.
- Lifecycle information: BIM supports the entire lifecycle of a facility, from conceptualization and design through construction and operation to eventual renovation or demolition. This makes it a valuable tool for asset management and maintenance.
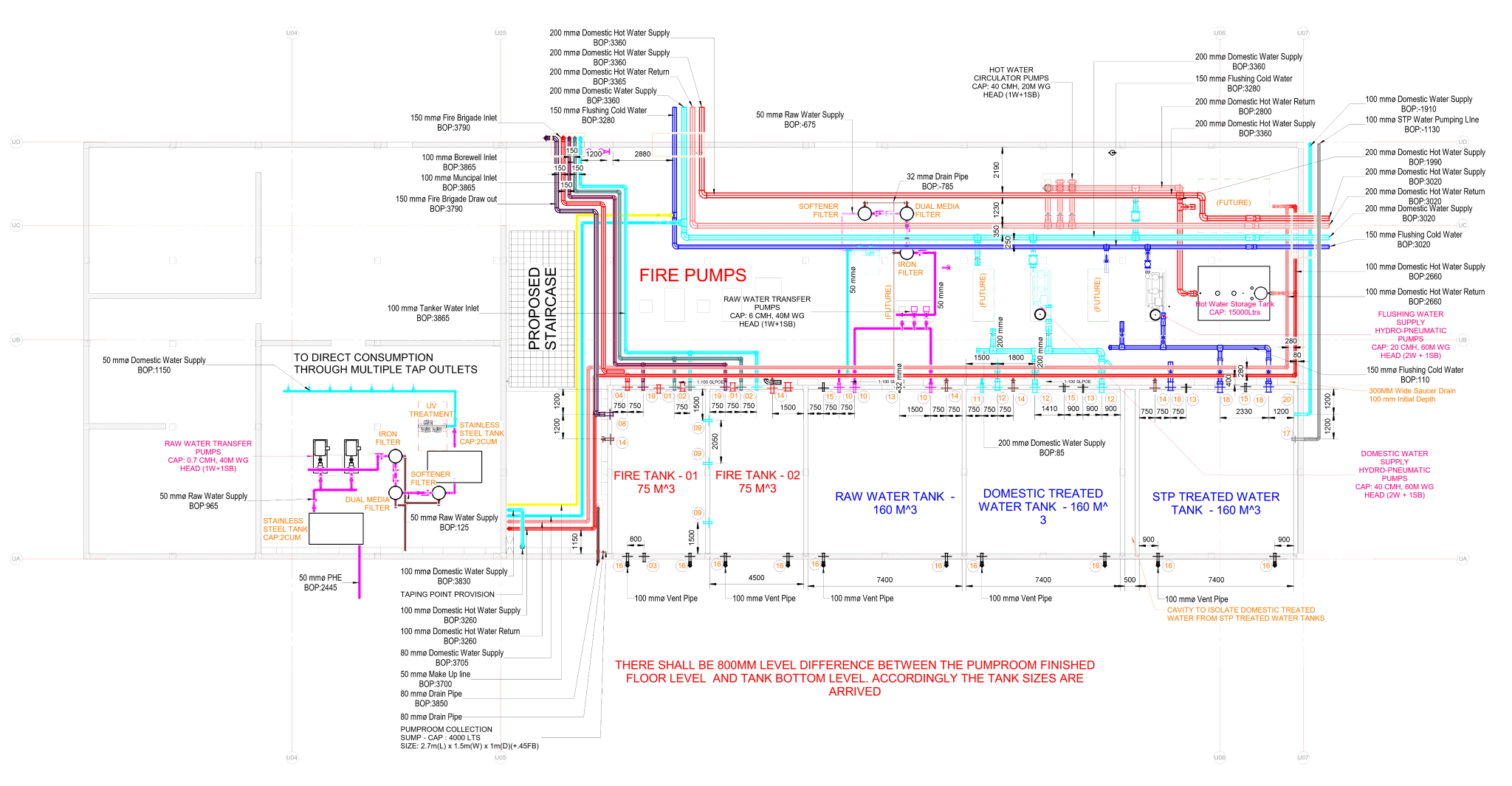
Building information modelling (BIM) is a transformative approach to the planning, design, construction, and management of buildings and infrastructure. Unlike traditional 2D drawings, BIM involves creating a digital model that encompasses not only the geometric representation of a structure but also a wealth of data related to its components, materials, systems, and performance attributes.
Some of the key components of BIM are:
- Geometry: BIM models include three-dimensional geometric representations of building elements, providing a visual understanding of the structure's form and layout.
- Data: BIM incorporates non-graphic information related to each building component. This can include material specifications, dimensions, cost data, performance characteristics, and maintenance requirements.
- Relationship: BIM enables the establishment of relationships and dependencies between different elements in the model. For example, connections between structural components or the impact of a change in one area on other aspects of the project.
- Collaboration: BIM facilitates collaboration among different stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers. This collaborative environment encourages real-time sharing of information and reduces the likelihood of errors.
- Lifecycle information: BIM supports the entire lifecycle of a facility, from conceptualization and design through construction and operation to eventual renovation or demolition. This makes it a valuable tool for asset management and maintenance.
Benefit of building information modelling:
- Improved communication: BIM enhances communication and coordination among project stakeholders by providing a centralized platform for information sharing. This reduces errors and facilitates smoother collaboration.
- Efficient design and construction: The 3D visualization and data-rich nature of BIM models help in identifying design conflicts and issues early in the process, minimizing rework during construction and reducing project delays and costs.
- Cost estimation and analysis: BIM allows for more accurate cost estimation by associating cost data with building components. It also enables the analysis of different design options to optimize project costs.
- Facility management: BIM's lifecycle perspective supports effective facility management by providing detailed information about each component, aiding in maintenance planning, and facilitating renovations or expansions.
As the industry continues to evolve, future trends in BIM include greater integration with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These advancements will further enhance the capabilities of BIM and contribute to more efficient and sustainable built environments.
In conclusion, building information modelling is a paradigm shift in the way the architecture, engineering, and construction industry approaches projects. It goes beyond traditional design methods by creating a comprehensive digital representation that serves as a single source of truth throughout the entire lifecycle of a building or infrastructure project. The widespread adoption of BIM is transforming the industry and driving improvements in collaboration, efficiency, and sustainability.