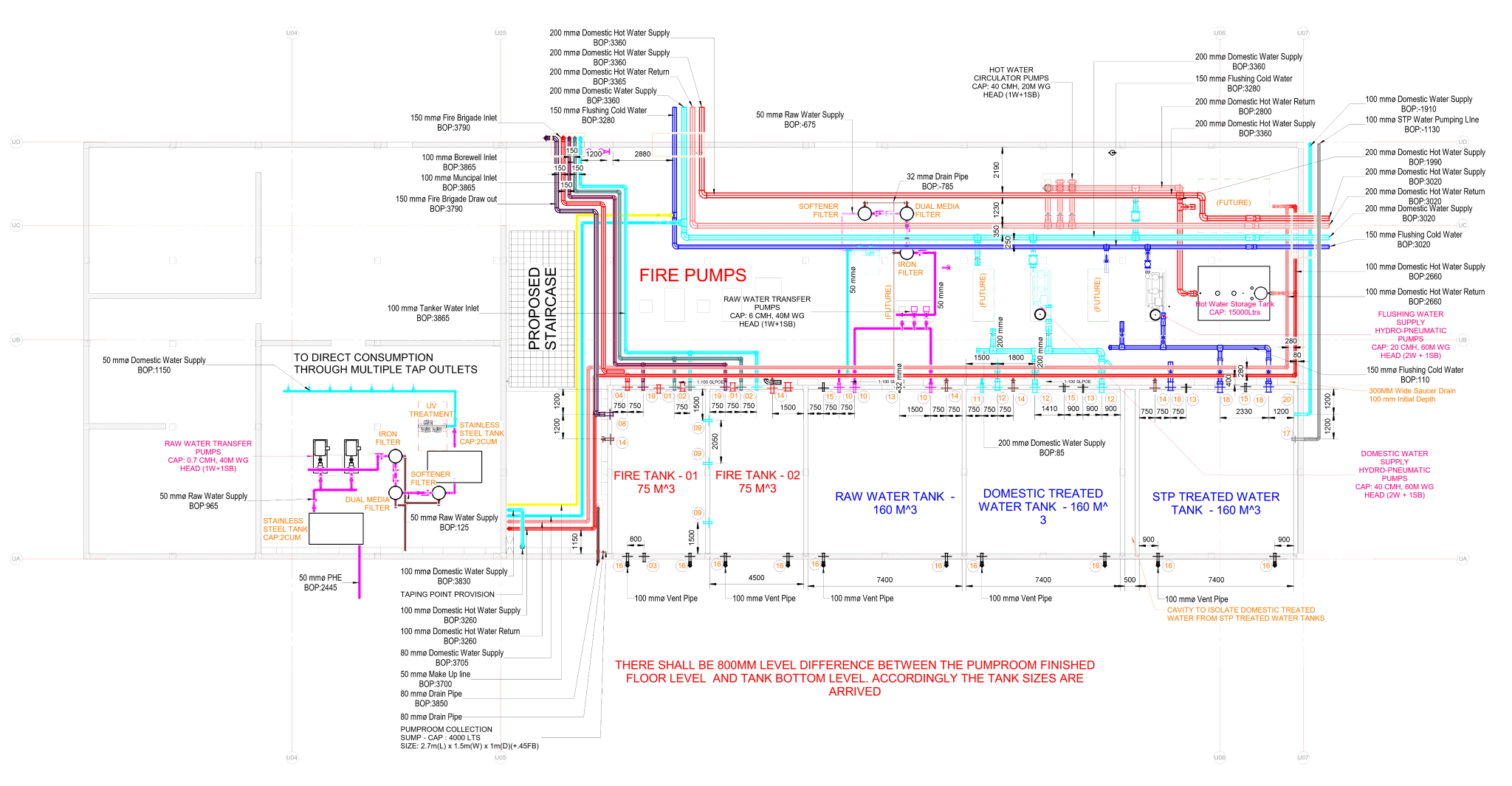
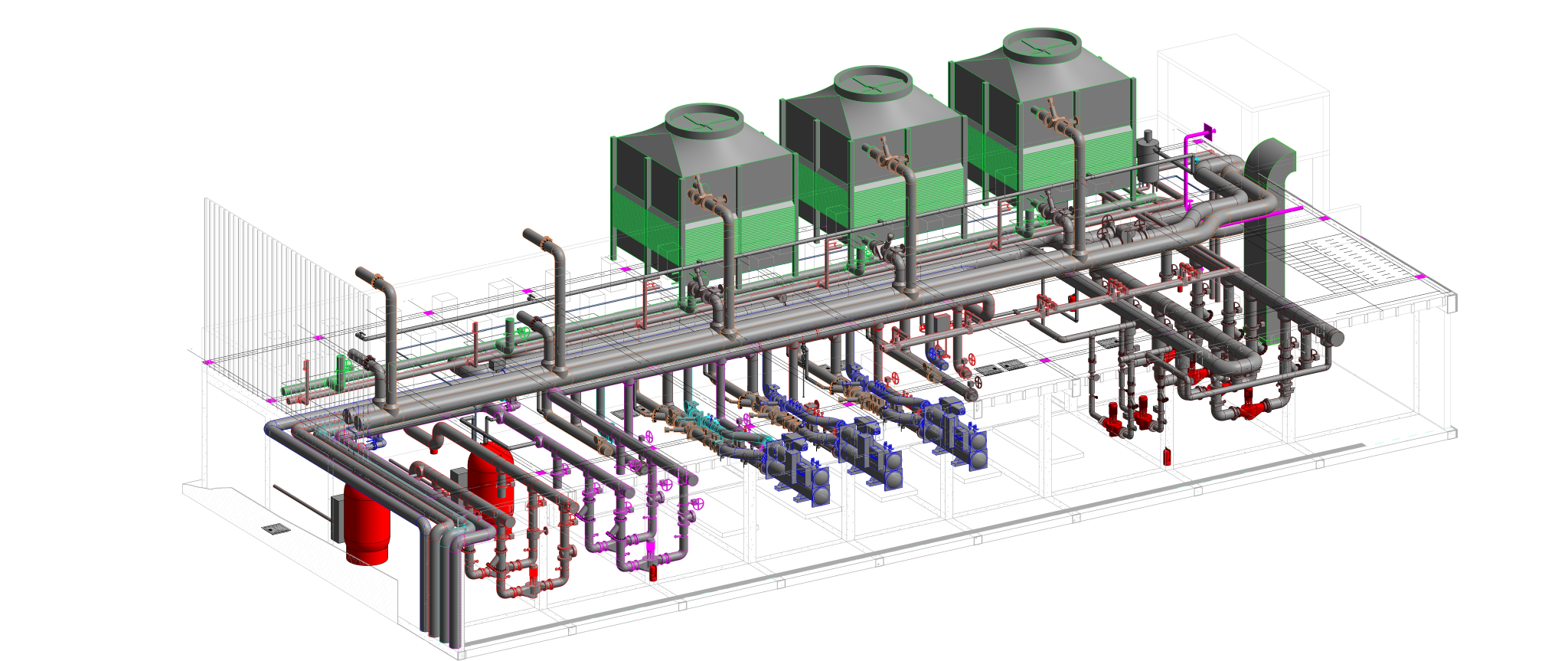
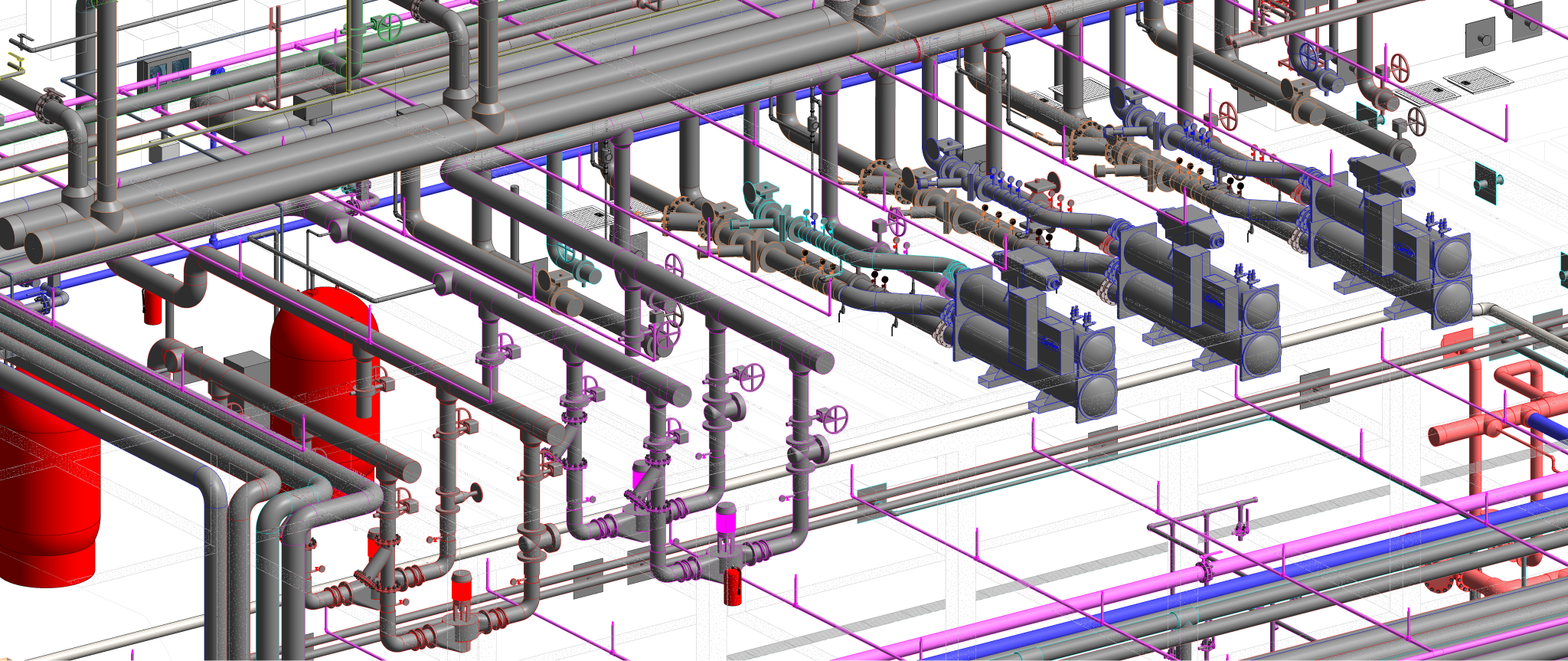
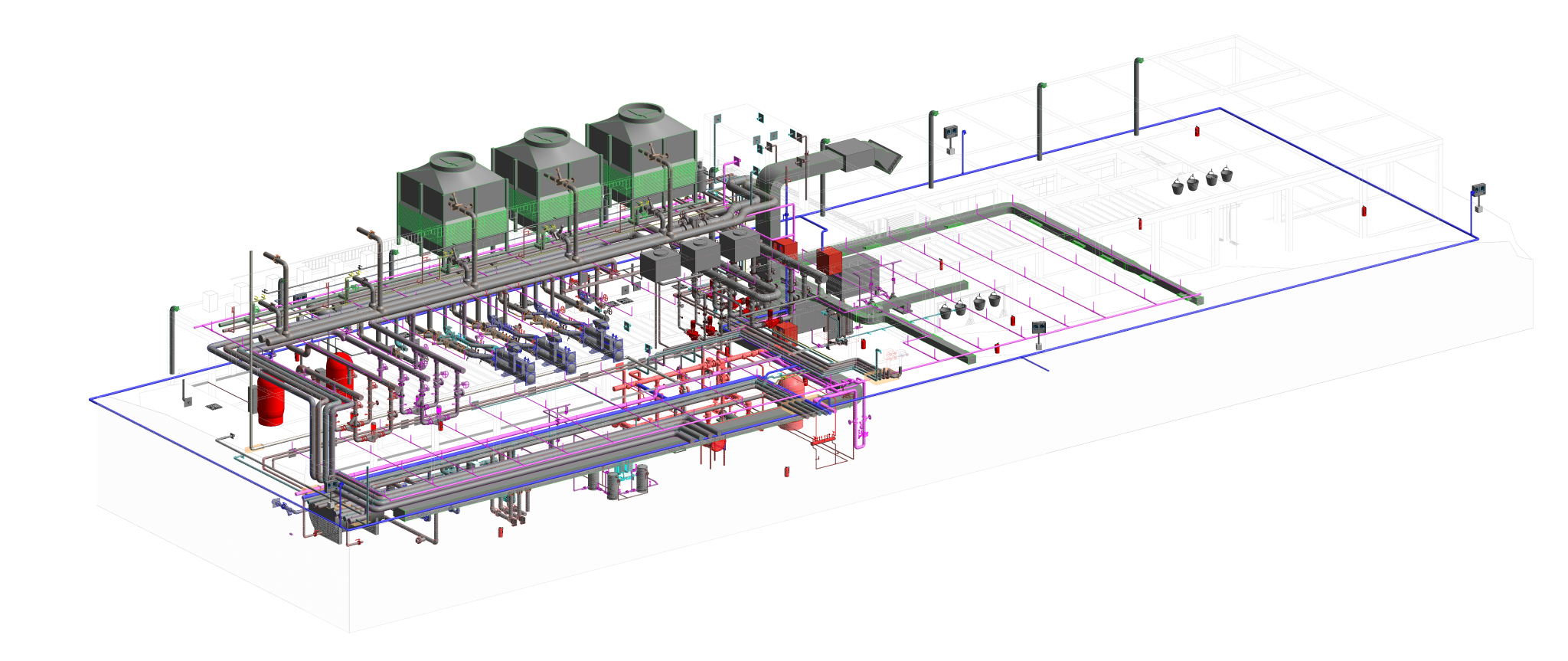
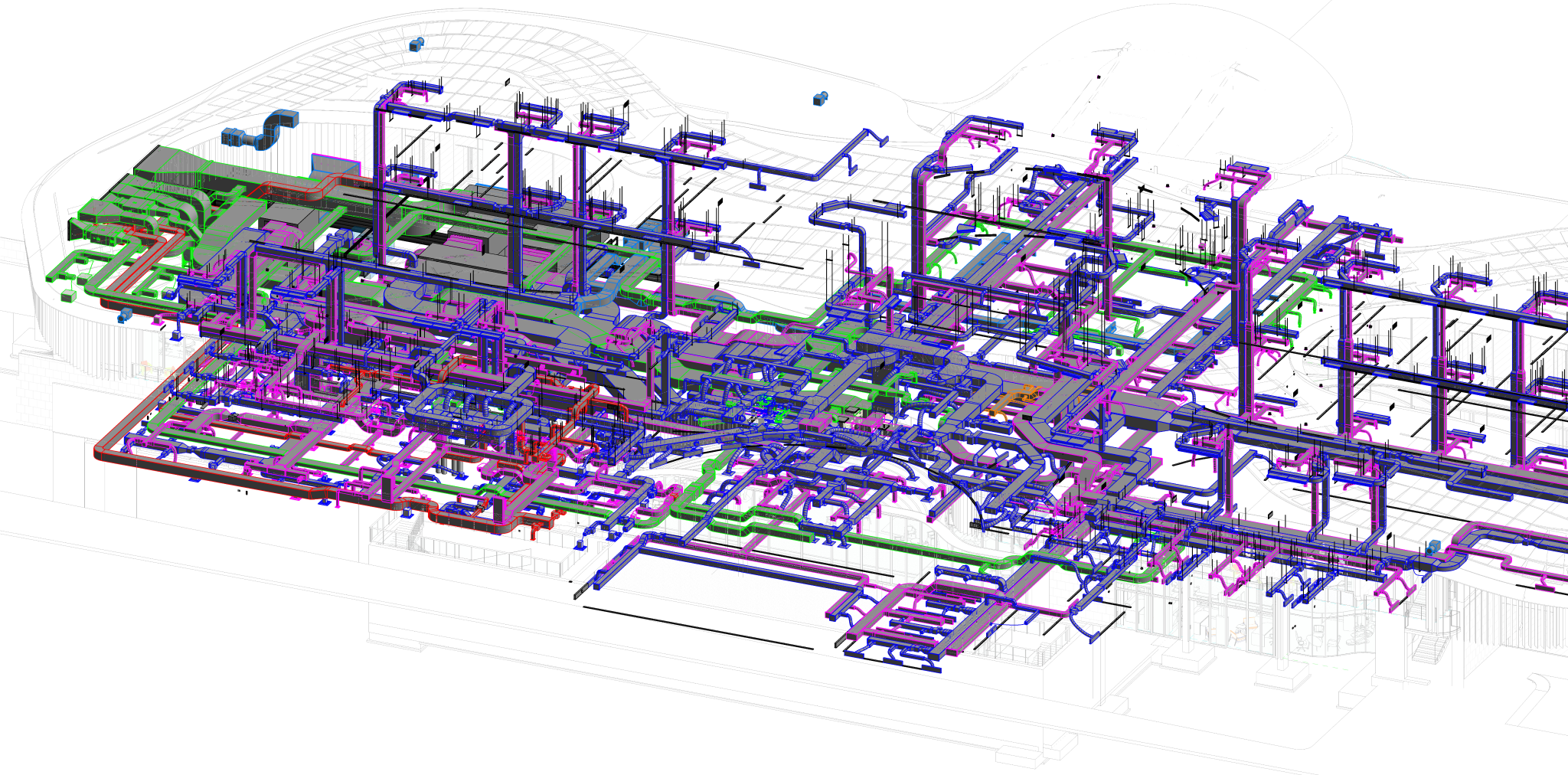
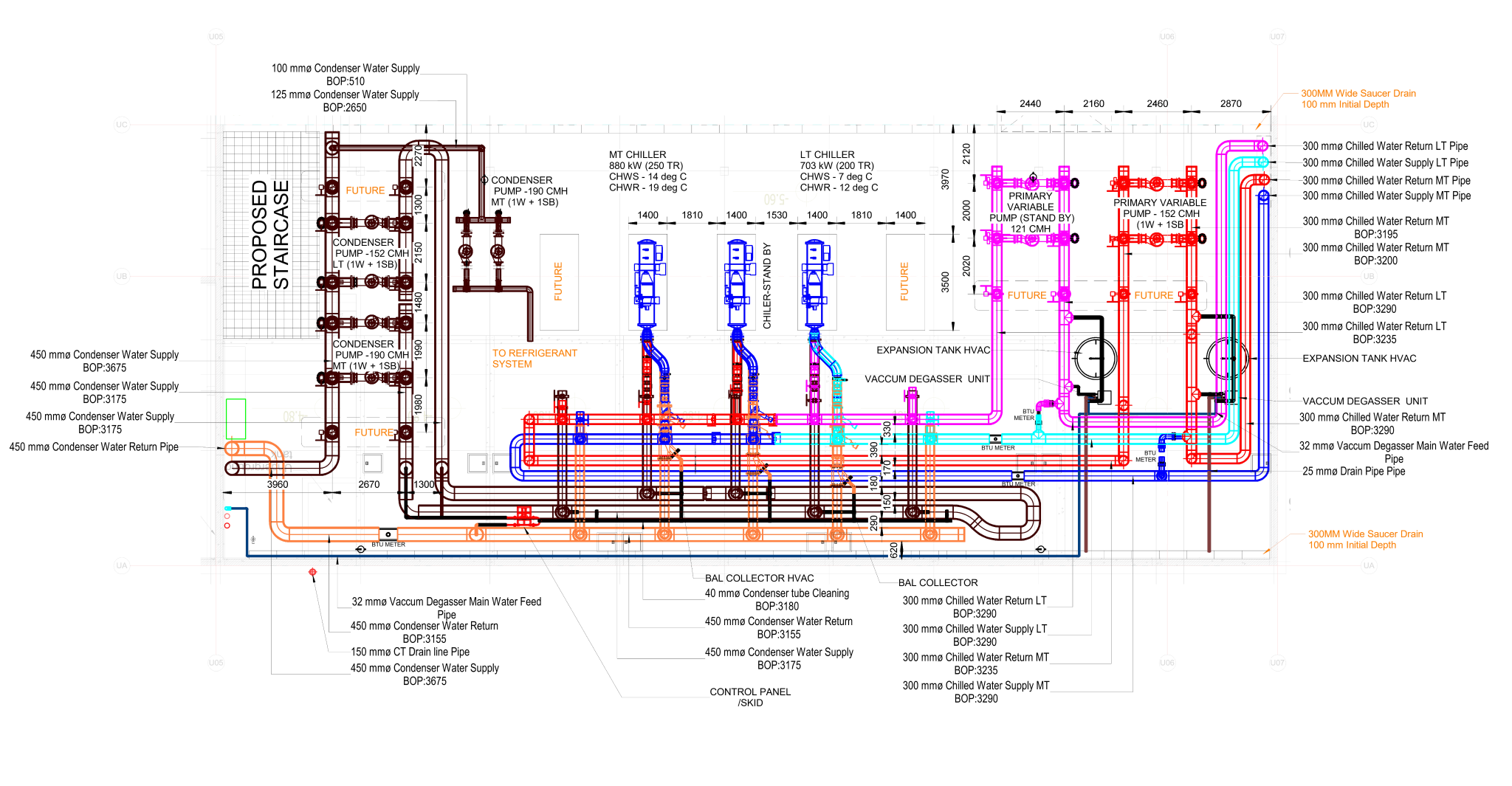
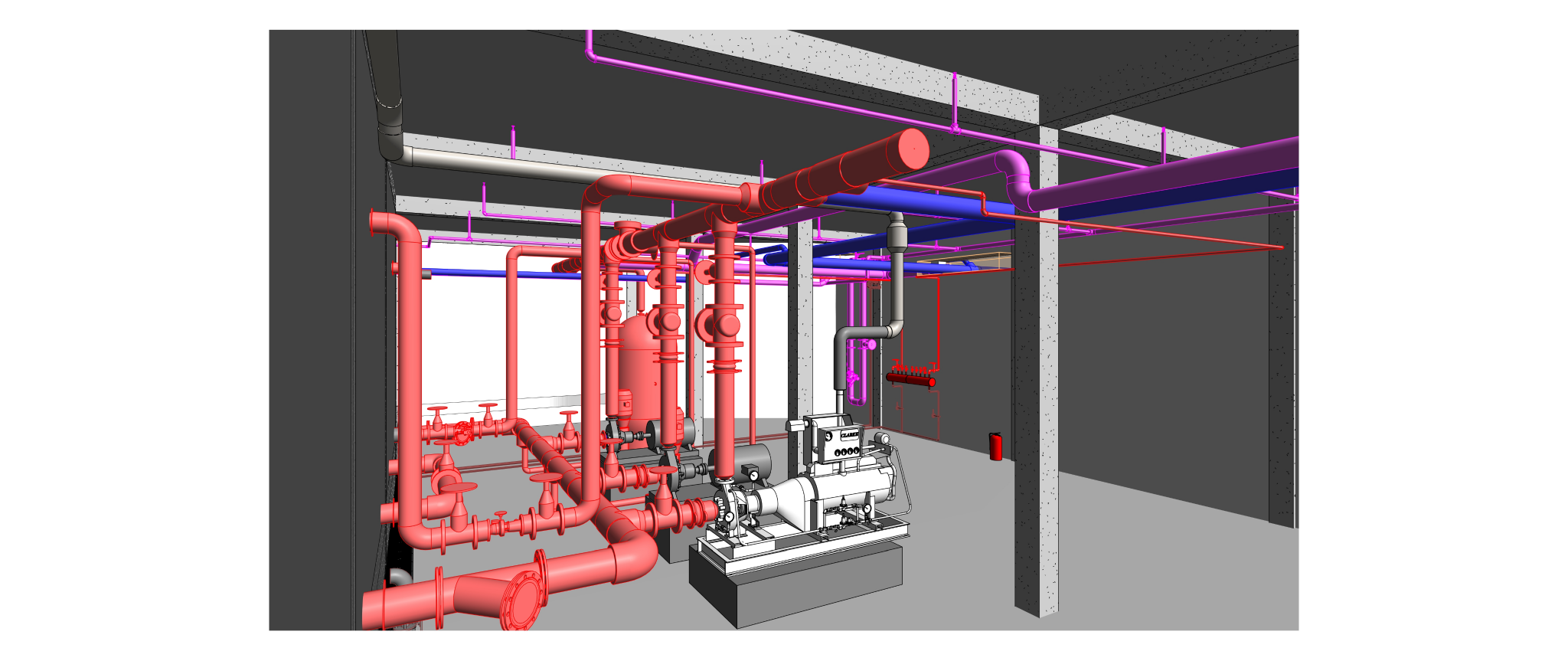
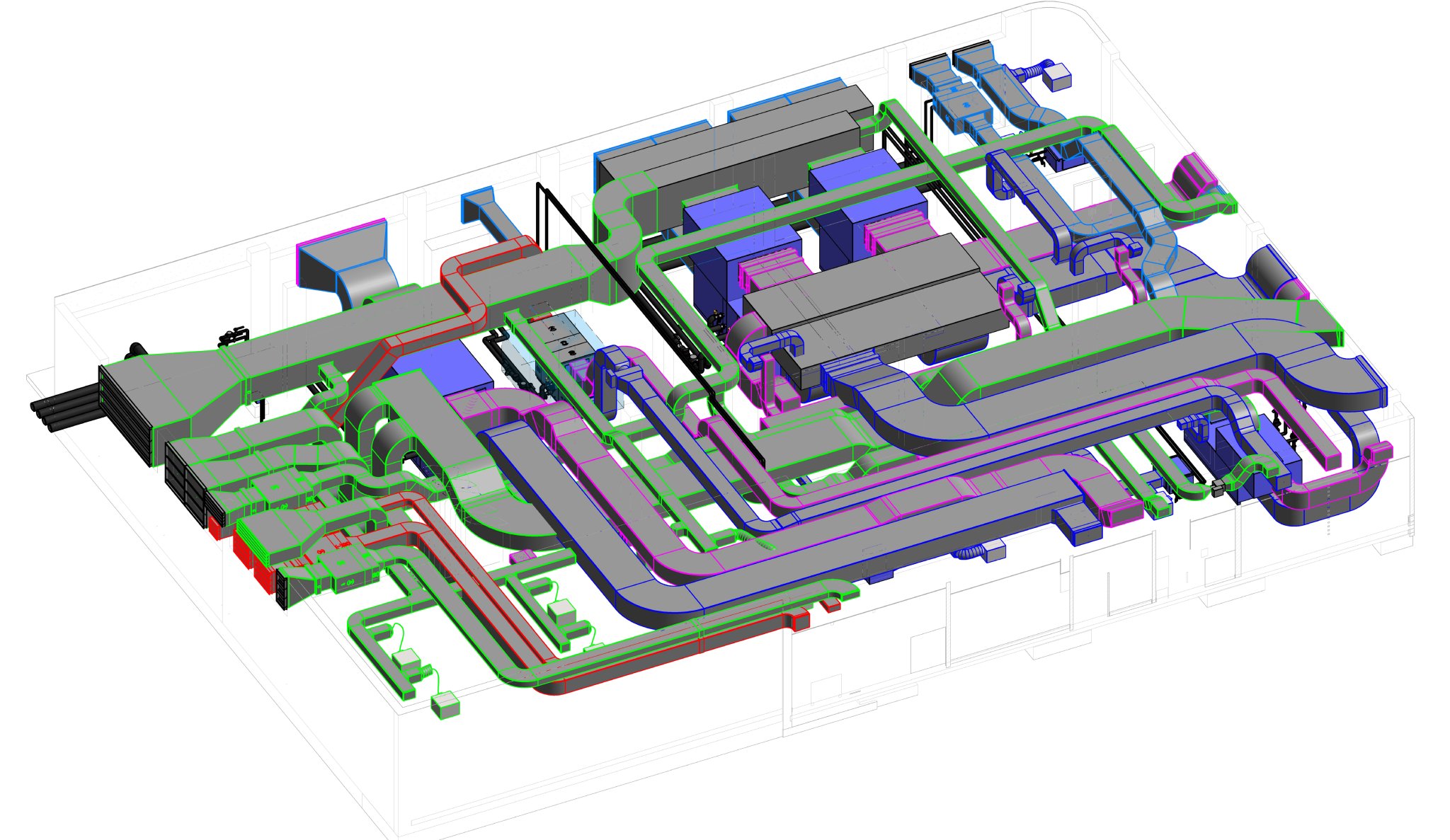
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) is a critical technology employed in buildings to regulate indoor environmental conditions, ensuring comfort and air quality. This comprehensive system addresses heating needs during colder periods, cools indoor spaces in warmer weather, and manages ventilation for fresh air circulation. Key components include furnaces or boilers for heating, air conditioners or heat pumps for cooling, and ventilation systems for air exchange. Ductwork facilitates the distribution of conditioned air, while thermostats control temperature settings. Humidity control, air filtration, and purification are integral for maintaining a healthy indoor environment. Advanced features, such as zoning, smart technology integration, and energy recovery, enhance efficiency and customization. Sustainable practices, including renewable energy integration and eco-friendly refrigerants, contribute to environmentally conscious HVAC solutions. Regular maintenance and proper design are essential for optimizing performance and prolonging the lifespan of HVAC systems, ensuring they meet the diverse needs of residential, commercial, and industrial spaces.
The principle of operation for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems involves the integrated management of temperature, humidity, air quality, and air circulation within a building. The key components and their functions are as follows:
- Heating: During the heating mode, a furnace or boiler generates heat by burning fuel (such as natural gas, oil, or using electricity) or through alternative methods like heat pumps. The generated heat is then distributed throughout the building via a system of ducts, pipes, or radiant systems.
- Ventilation: Ventilation is crucial for maintaining indoor air quality. Fresh outdoor air is brought into the building, and stale indoor air is expelled. Mechanical ventilation systems, which include fans and ducts, help in the controlled exchange of air.
- Air conditioning: Air conditioners or heat pumps operate on a refrigeration cycle. They remove heat from indoor air, releasing it outside, and cool the air before redistributing it indoors. This process also removes humidity from the air, contributing to a more comfortable indoor environment.
- Air distribution: Ductwork, registers, and grilles play a key role in distributing conditioned air throughout the building. Different zones can be established for more precise temperature control.
- Humidity control: Humidity control is achieved through the use of dehumidifiers or humidifiers, depending on the need to remove or add moisture to the air.
In summary, the principle of operation for HVAC systems involves the coordinated functioning of various components to achieve optimal indoor comfort and air quality based on user preferences and environmental conditions.