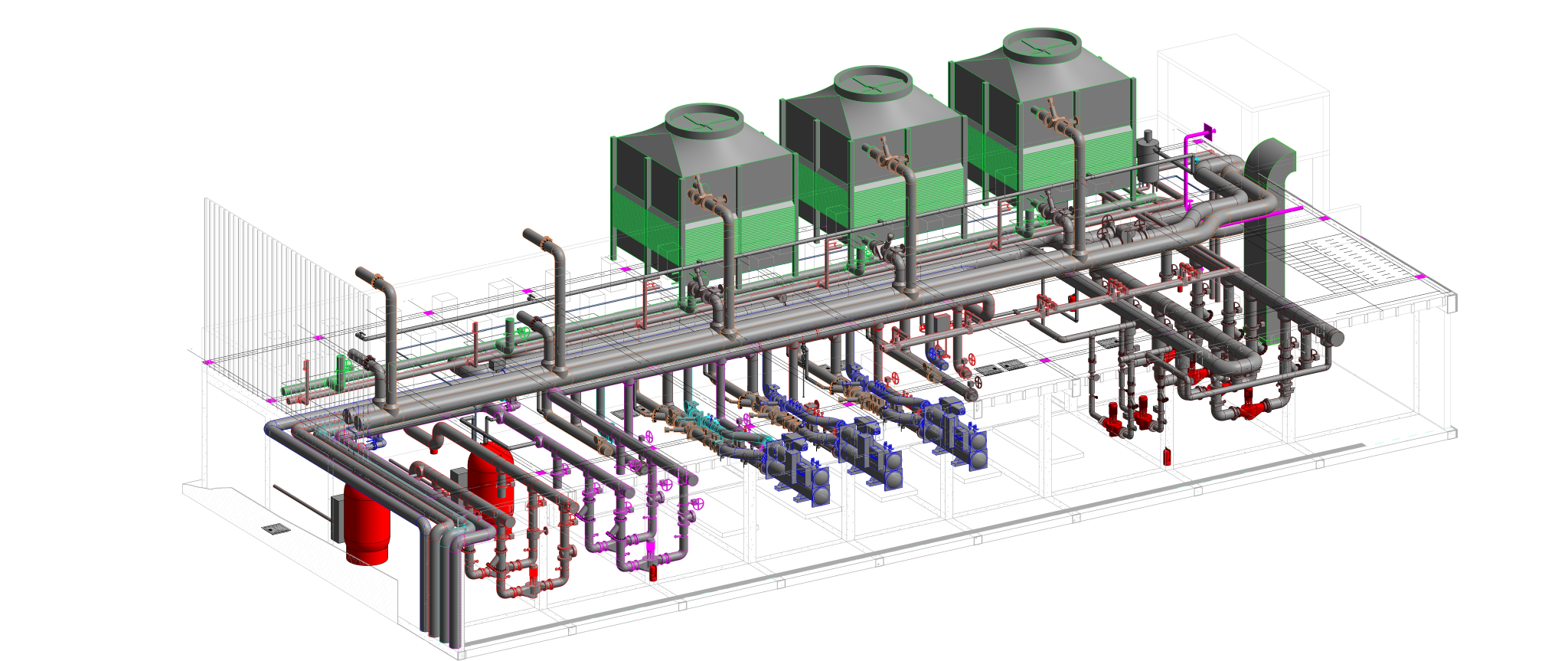
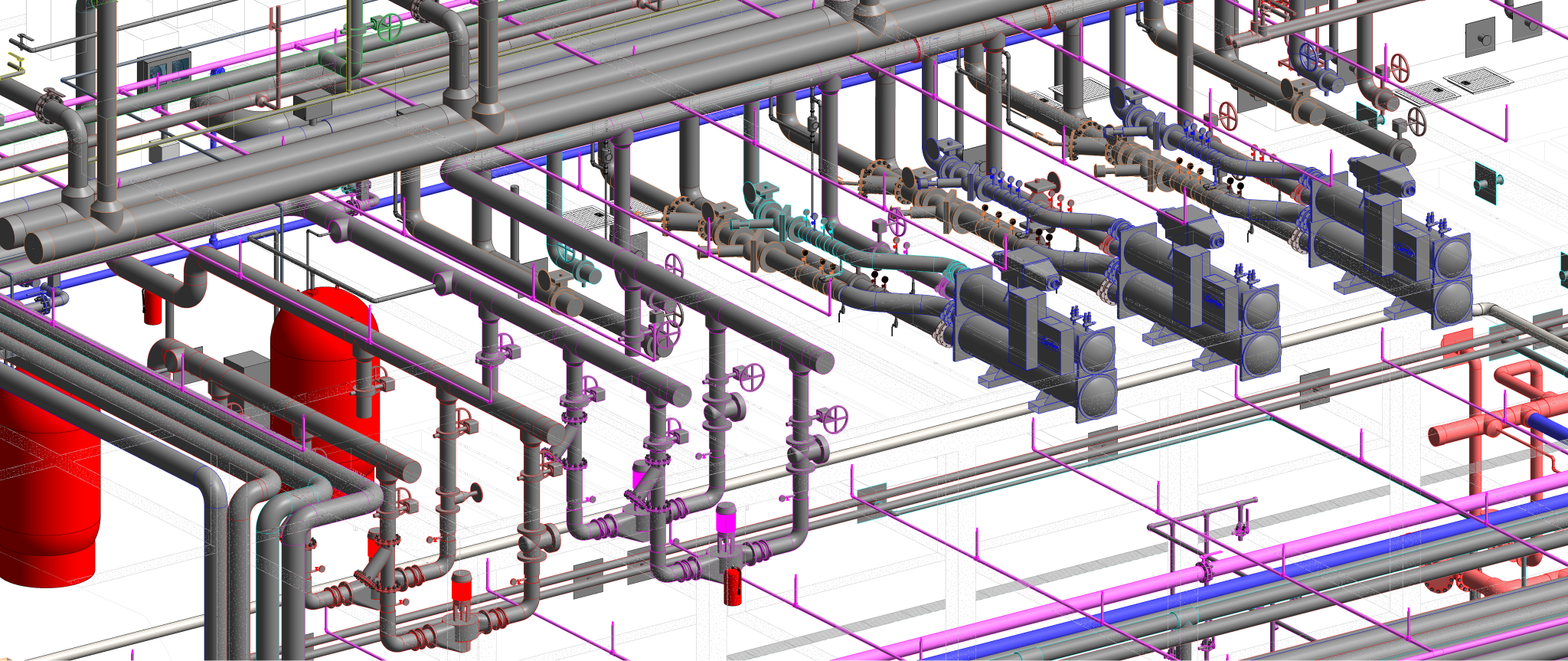
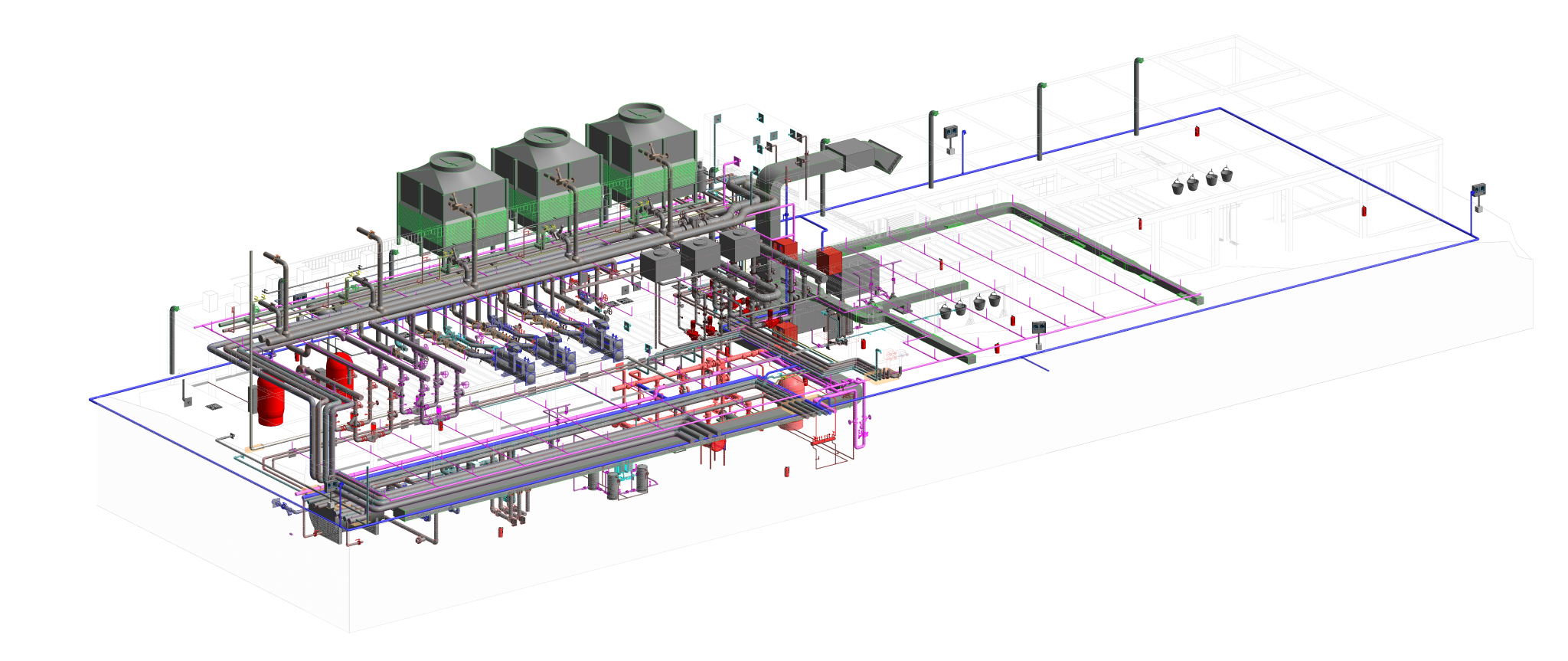
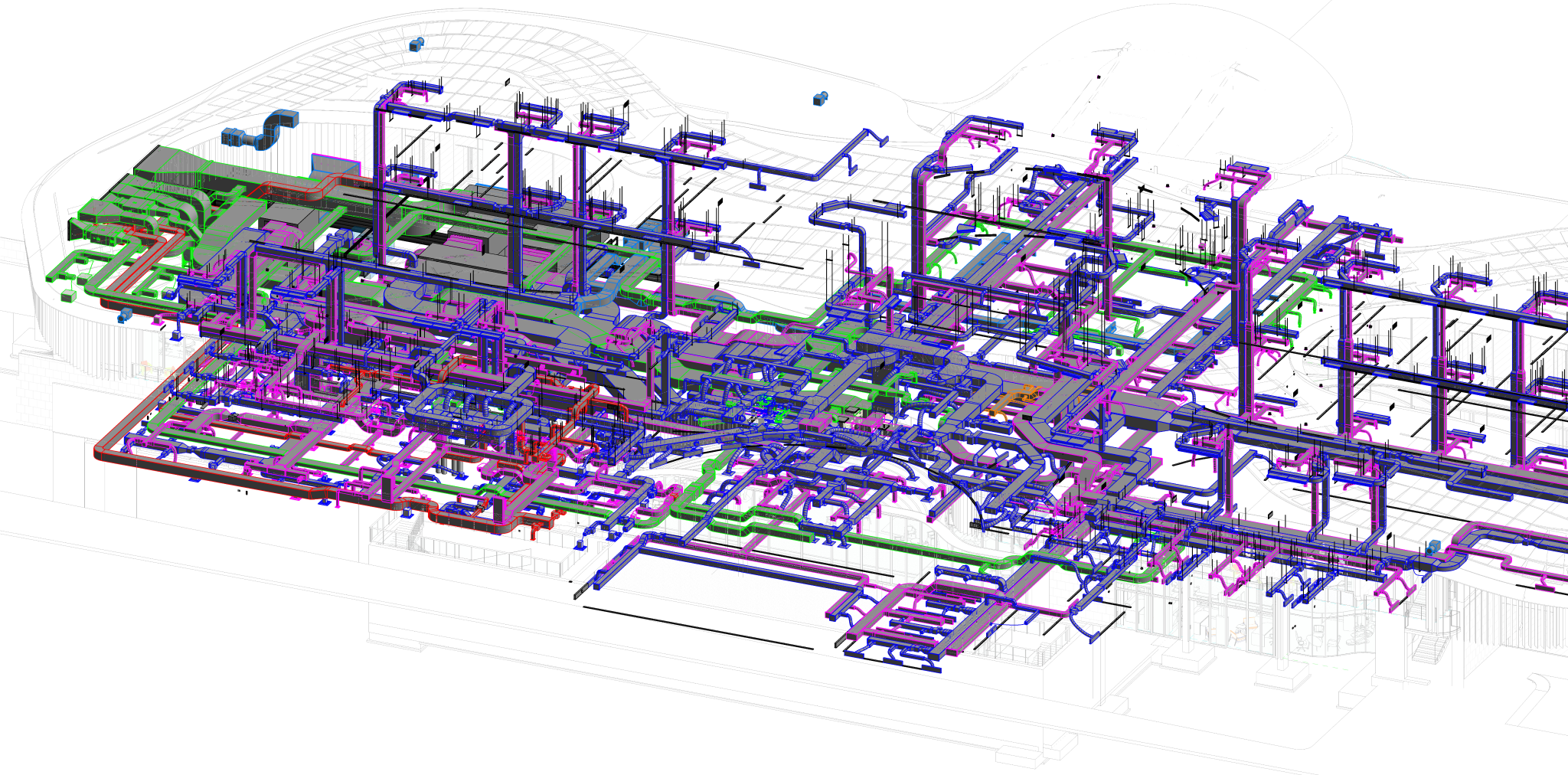
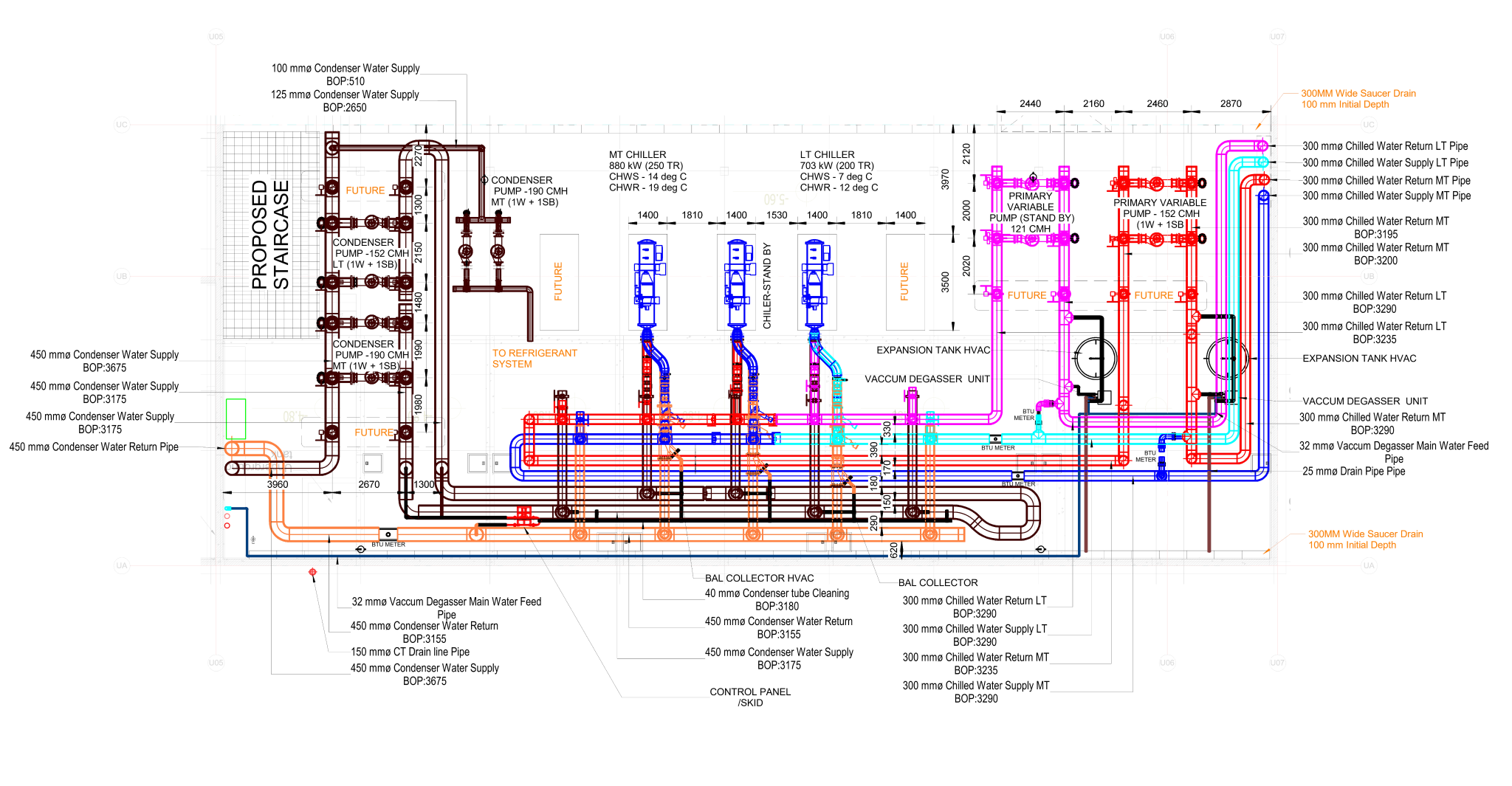
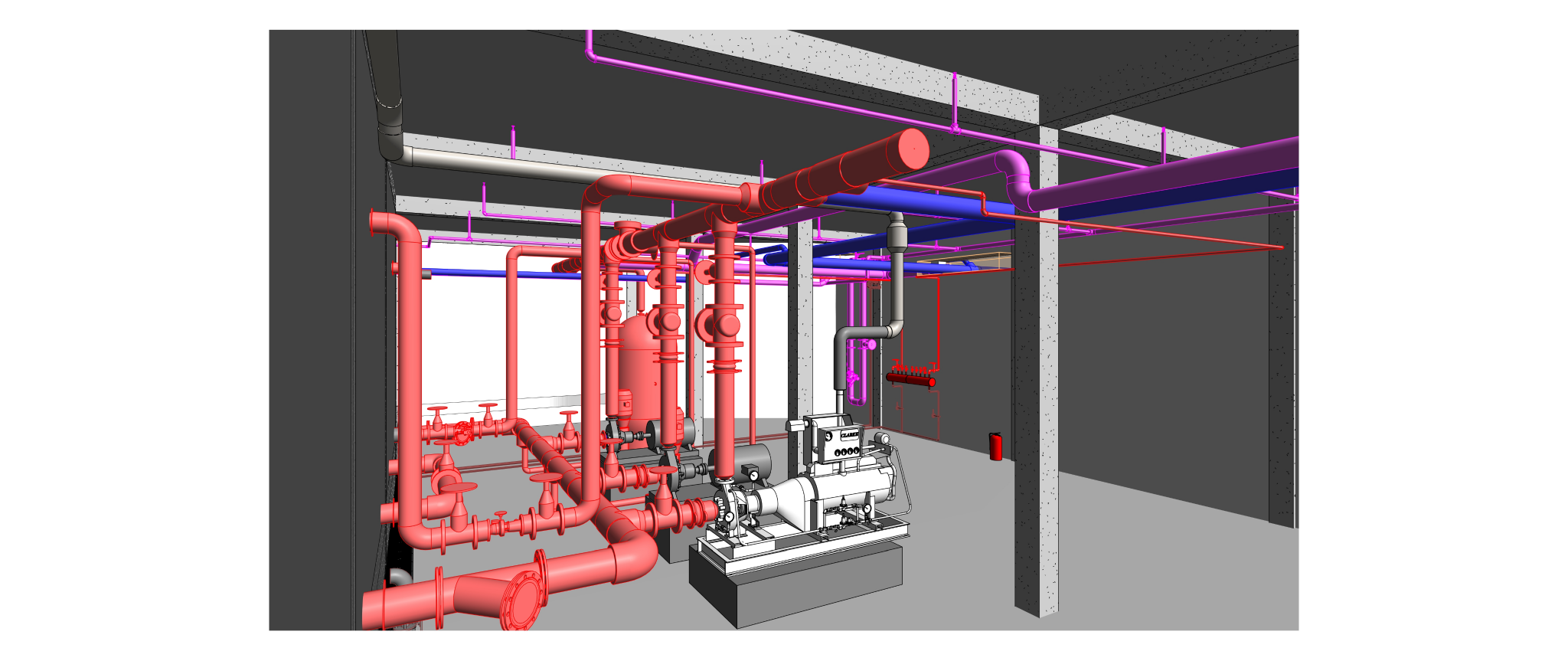
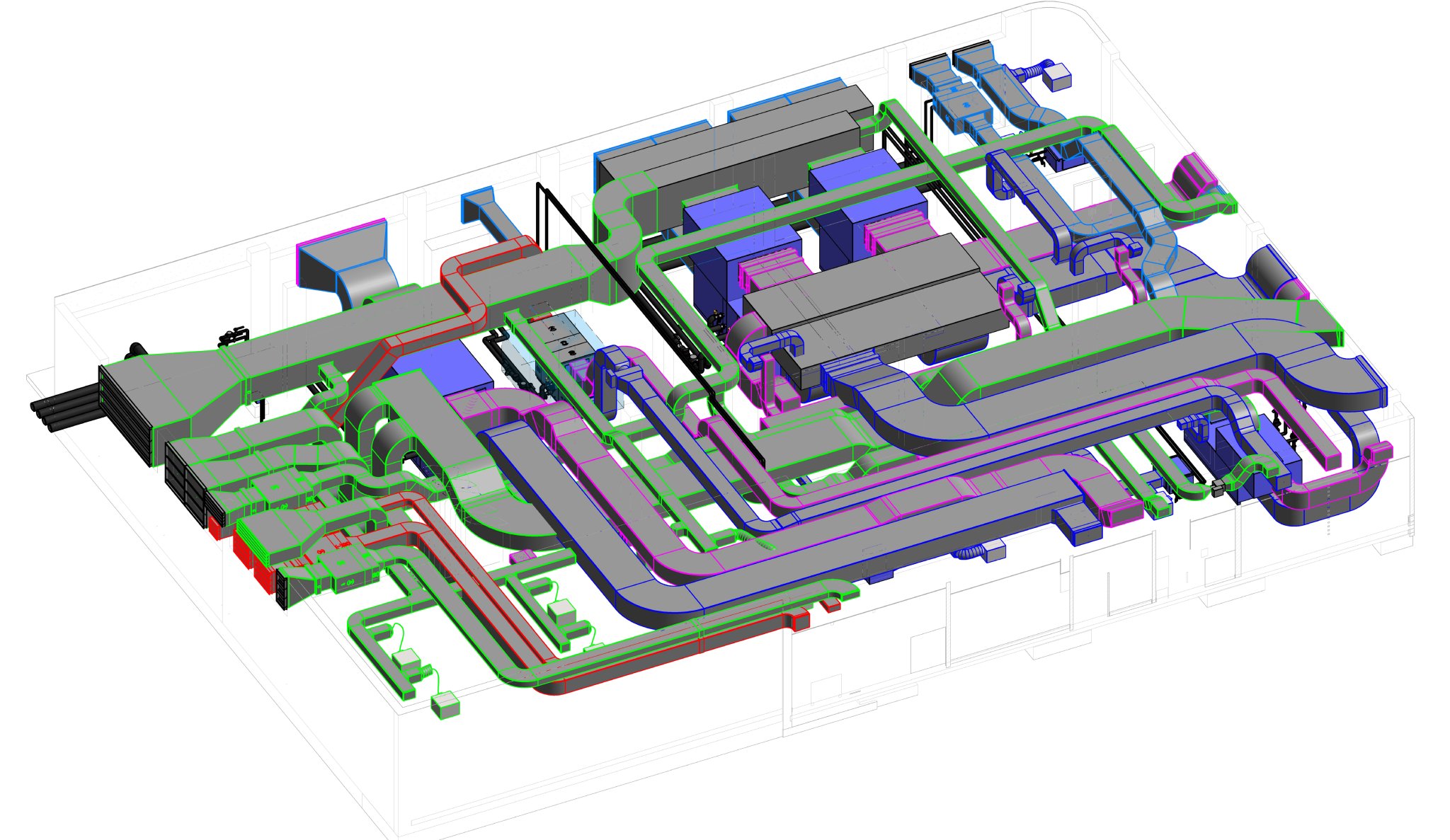
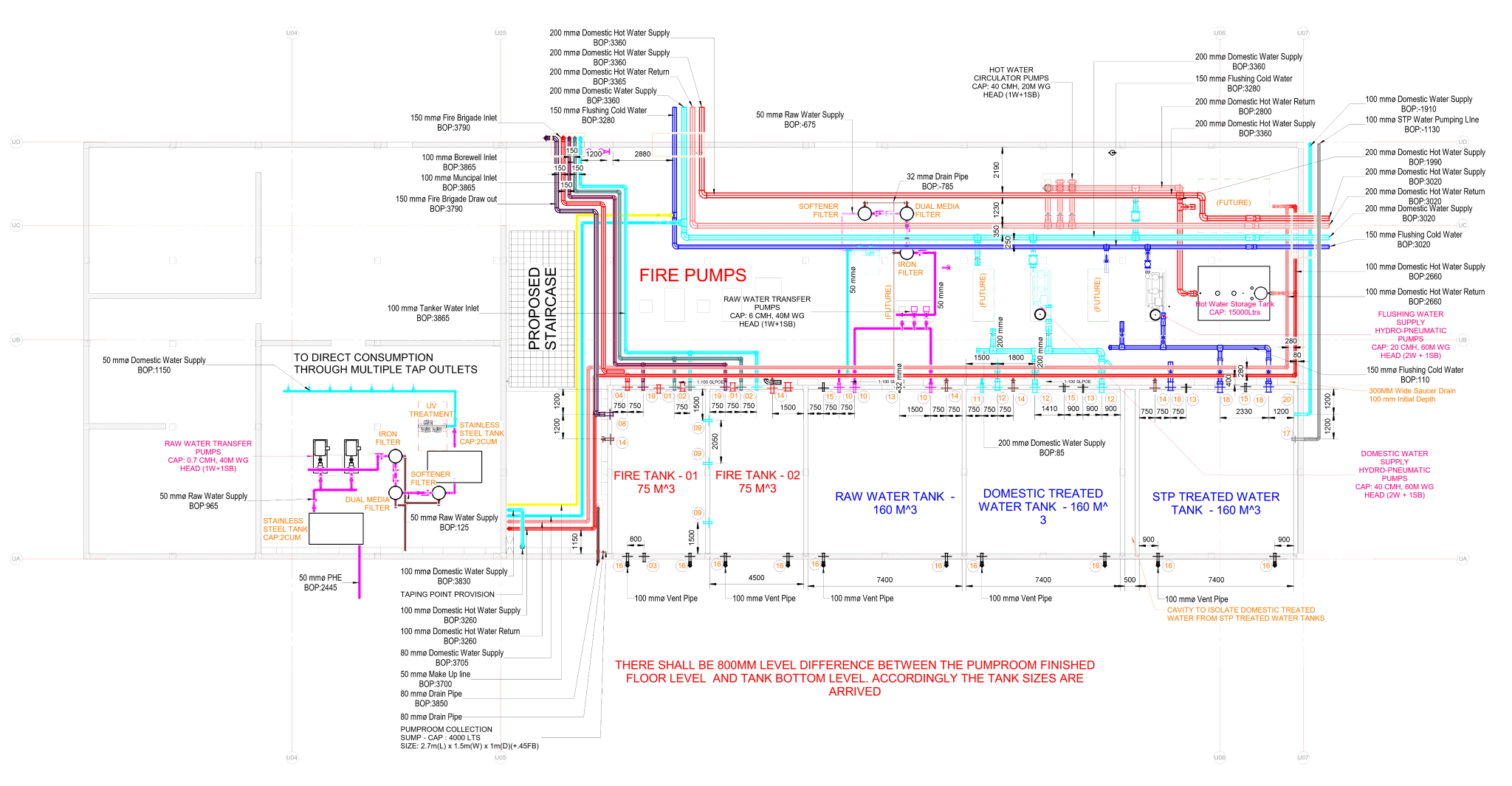
Radiant cooling is a method of cooling indoor spaces by removing heat from the building using the principles of thermal radiation. Unlike traditional air conditioning systems that rely on convection to cool the air, radiant cooling systems transfer heat from the indoor environment to a cooled surface, which then radiates the heat away.
This process can be applied to various building elements, such as floors, walls, or ceilings.
Here are some key points about radiant cooling:
- Principle of Operation:
- Radiant cooling systems typically use chilled water or other cooling fluids circulating through pipes or panels in building surfaces.
- Heat from the indoor environment is absorbed by the cooled surface, and the surface then radiates this heat away.
- The radiant exchange between the cooled surface and other surfaces (including people and objects) helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
- Types of Radiant Cooling Systems:
- Hydronic systems: These systems use water as the cooling fluid, circulating it through pipes or panels.
- Radiant baffle systems: These are passive convection/radiant cooling devices mounted in the ceiling. They rely on natural convection and radiation to cool the indoor space.
- Advantages:
- Radiant cooling systems can be more energy-efficient than traditional air conditioning because they operate at higher chilled water temperatures.
- Radiant cooling provides a more even distribution of temperatures across a space, minimizing hot and cold spots. This can contribute to a more comfortable indoor environment.
- Radiant cooling systems are often quieter than traditional HVAC systems because they don't rely on noisy fans or blowers to distribute air within the conditioned space.
- Radiant systems offer flexibility in architectural design, as they don't require large ductwork or extensive space for equipment. This flexibility can be advantageous in retrofitting existing buildings or designing new, innovative structures.
- With reduced air movement, there is less likelihood of stirring up dust or other particulate matter. This can contribute to better indoor air quality.
- Radiant systems can be designed to provide both cooling and heating, offering a year-round solution for climate control.
- Radiant systems can be integrated with renewable energy sources, such as solar thermal or geothermal systems, sea water air-conditioning enhancing their sustainability and reducing reliance on non-renewable energy.
- Applications:
- Radiant cooling is used in a variety of settings, including commercial buildings, hospitality, healthcare, residential homes, and industrial facilities.
- It is often integrated with other sustainable building practices to create energy-efficient and environmentally friendly structures.